What are crucial facts related to liver cancer?
What Is Liver Cancer?
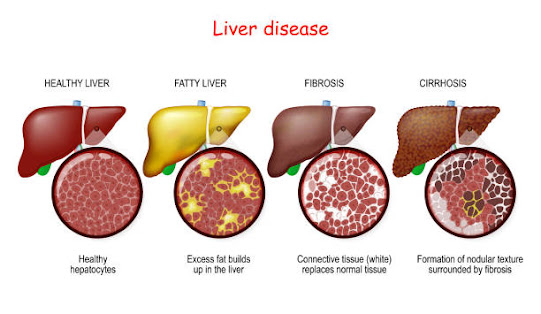
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the liver. It is a type of malignant tumor that originates in the liver or spreads to the liver from other parts of the body. The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying the body, producing bile for digestion, and storing essential nutrients. When cancer cells develop in the liver, they disrupt its normal functioning, potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
Types of Liver Cancer
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): This is the most common type of liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% to 85% of cases. HCC usually develops in individuals with underlying liver diseases such as cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B or C infection.
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: This type of liver cancer originates in the cells lining the bile ducts within the liver. It accounts for around 10% to 20% of liver cancer cases.
Hepatoblastoma: Hepatoblastoma is a rare type of liver cancer that primarily affects children under the age of 5. It typically responds well to treatment, and the prognosis is generally favorable.
Angiosarcoma and Hemangiosarcoma: These are rare types of liver cancer that develop in the blood vessels of the liver. They tend to grow rapidly and have a poorer prognosis compared to other types.
Causes and Risk Factors
Liver cancer can arise from various factors and underlying conditions. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with liver cancer can help in its prevention and early detection. Some crucial facts related to the causes and risk factors of liver cancer include:
Chronic Hepatitis B or C Infection: Individuals with long-term infection of hepatitis B or C viruses have a higher risk of developing liver cancer. It is important to undergo regular screenings and seek appropriate medical management for these conditions.
Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis, a condition characterized by scarring of the liver, increases the risk of liver cancer. Common causes of cirrhosis include excessive alcohol consumption, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and chronic viral hepatitis.
Alcohol Abuse: Heavy and prolonged alcohol consumption can significantly increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Limiting alcohol intake and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate this risk.
Aflatoxins: Aflatoxins are toxic substances produced by certain types of molds that commonly contaminate peanuts, corn, and other crops. Prolonged exposure to aflatoxins increases the risk of liver cancer.
Obesity and Diabetes: Obesity and diabetes are known risk factors for various types of cancer, including liver cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, and managing diabetes can lower the risk of developing liver cancer.
Hereditary Conditions: Certain inherited liver diseases, such as hereditary hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease, can increase the risk of liver cancer. Regular screenings and genetic counseling may be recommended for individuals with these conditions.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Early detection of liver cancer is crucial for successful treatment and improved outcomes. However, liver cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms may manifest:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
If you experience any of these symptoms or have a higher risk of liver cancer, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation. Early detection methods, such as imaging tests, blood tests, and liver biopsies, can help confirm the diagnosis and guide further treatment decisions.
Diagnosis and Staging
When liver cancer is suspected, various diagnostic procedures are employed to determine the extent and stage of the disease. These may include:
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and angiography, help visualize the liver and identify any tumors or abnormalities.
Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure specific liver enzymes and tumor markers, which provide valuable information about liver function and the presence of cancerous cells.
Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the liver for laboratory analysis. It helps confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type and stage of liver cancer.
Staging: Staging liver cancer helps determine the extent of its spread. The most commonly used staging system for liver cancer is the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, which takes into account tumor size, number of tumors, liver function, and overall health status.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for liver cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the disease, the underlying liver function, and the patient's overall health. Treatment options for liver cancer may include:
Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor, known as a liver resection, is a potential treatment option for localized liver cancer. In cases where the cancer has spread, liver transplantation may be considered.
Ablation Therapy: Ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, and ethanol injection, destroy cancer cells using heat or cold. These procedures are suitable for small tumors and patients who are not eligible for surgery.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other approaches.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is commonly used for advanced liver cancer or as a palliative treatment to alleviate symptoms.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy utilizes drugs that specifically target cancer cells' molecular abnormalities, inhibiting their growth and spread. These therapies are often used in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps stimulate the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It has shown promising results in certain cases of advanced liver cancer.
Looking for advanced treatment for Liver Cancer?
Book an appointment with Dr. Sushil Kumar Jain, He is one of the most experienced Gastroenterologists in Jaipur, having more than 16+ years of experience in this field. provide world-class treatment for gastro and liver diseases at ACE Gastro Super-Speciality Clinic. You can directly book an appointment at 94620 67445.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What are the main risk factors for liver cancer?
A: The main risk factors for liver cancer include chronic hepatitis B or C infection, cirrhosis, excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to aflatoxins, obesity, diabetes, and certain hereditary conditions.
Q: Can liver cancer be prevented?
A: While it is not always possible to prevent liver cancer, certain measures can reduce the risk. These include getting vaccinated against hepatitis B, practicing safe sex, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular screenings for liver diseases.
Q: How is liver cancer diagnosed?
A: Liver cancer is diagnosed through various methods, including imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI), blood tests (liver enzymes and tumor markers), and liver biopsy.
Q: What are the treatment options for liver cancer?
A: Treatment options for liver cancer include surgery, ablation therapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the stage of the disease, liver function, and overall health.
Q: What is the prognosis for liver cancer?
A: The prognosis for liver cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the disease at diagnosis, the effectiveness of treatment, the underlying liver function, and the individual's overall health. Early detection and appropriate treatment can improve the prognosis.
Q: How can I support a loved one with liver cancer?
A: Supporting a loved one with liver cancer involves providing emotional support, accompanying them to medical appointments, helping with daily tasks, and encouraging them to follow the prescribed treatment plan. It is also important to educate yourself about the disease and be a source of encouragement and positivity.
Conclusion
Understanding the crucial facts related to liver cancer is essential for early detection, effective treatment, and improved outcomes. This article has provided valuable insights into the various aspects of liver cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to maintain liver health, individuals can minimize their risk of developing liver cancer and seek timely medical intervention when needed. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding liver cancer and its management.
Comments
Post a Comment